System Biosciences
ExoQuick exosome precipitation solution (20 ml)
- SKU:
- EXOQ20A-1
- Availability:
- Usually Shipped in 5 Working Days
- Size:
- 20 ml
- Shipping Temperature:
- RT, Blue Ice, or Dry Ice
Description
ExoQuick exosome precipitation solution (20 ml). Cat# EXOQ20A. Supplier: SBI System Biosciences

Overview
A better way to isolate exosomes
"We therefore pursued the ExoQuick® method for further study, as these samples required much less sample input, a key benefit when working with clinical samples and mouse models1."
Need exosomes? SBI's ExoQuick, original formulation, enables high-throughput, quantitative isolation of exosomes from low volumes (as little as 100 µl) of serum, plasma, or ascites fluid. Compatible with a wide variety of downstream applications, ExoQuick is an effective and proven alternative to ultracentrifugation1-3.
ExoQuick’s fast, ultracentrifugation-free method:- Saves time and labor
- Is easily scalable
- Conserves precious sample
- Delivers high yields of functional, high quality exosomes
- Can be used to isolate exosomes for a wide range of downstream applications, including biomarker studies, exosomal miRNA profiling, exosomal proteomics, exosomal lipidomics/metabolomics, functional studies, such as in cell-to-cell signaling, basic biology, such as role in tumorigenesis.


- Chugh PE, et al. Systemically Circulating Viral and Tumor-Derived MicroRNAs in KSHV-Associated Malignancies. PLoS Pathog. 2013.9(7): e1003484. PMCID: PMC3715412.
- Umezu T, et al. Leukemia cell to endothelial cell communication via exosomal miRNAs. Oncogene. 2013 May 30.32(22):2747-55. PMID: 22797057.
- Sohel MM, et al. Exosomal and Non-Exosomal Transport of Extra-Cellular microRNAs in Follicular Fluid: Implications for Bovine Oocyte Developmental Competence. PLoS One. 2013 Nov 4.8(11):e78505. PMCID: PMC3817212.
- Antes T, et al. Methods for Microvesicle Isolation and Selective Removal. Patent No.: US 9,005,888 B2.
How It Works
High-throughput, quantitative exosome recovery
ExoQuick can be used to purify exosomes from plasma1, serum2, and malignant ascites3. With a simple workflow involving minimal hands-on time and low input sample volume requirements, ExoQuick is an excellent option for researchers who need to purify multiple exosome samples and/or samples from small animal models or clinical research samples.
To isolate exosomes from cleared serum, plasma, or ascites fluid, simply:
- Add an appropriate volume of ExoQuick to as little as 100 µl sample
- Incubate for at least one hour at 4°C
- Isolate exosomes with a 30-minute low-speed spin (1500 g).
Isolated exosomes can be found in the pellet and resuspended in an appropriate solution.

You can verify the presence of exosomes with a number of different methods, including Western blotting for general exosome markers (CD63, CD9, CD81, and HSP70), NanoSight analysis, or EM (learn about different ways to detect exosomes and more in our Exosome Basics Guide).
The Bottom Line
With ExoQuick, you can obtain high-quality exosomes from most biofluids using a protocol that can easily be performed on multiple samples and requires very low volumes of input sample.
REFERENCES
- Chugh PE, et al. Systemically Circulating Viral and Tumor-Derived MicroRNAs in KSHV-Associated Malignancies. PLoS Pathog. 2013. 9(7): e1003484. PMCID: PMC3715412.
- Epple LM, et al. Medulloblastoma Exosome Proteomics Yield Functional Roles for Extracellular Vesicles. PLoS ONE. 2012. 7(7): e42064. PMCID: PMC3407172.
- As featured in: Exosome Isolation for Proteomic Analyses and RNA Profiling Douglas D. Taylor, Wolfgang Zacharias and Cicek Gercel-Taylor, Serum/Plasma Proteomics, Methods in Molecular Biology, 2011, Volume 728, Part 4, 235-246.
Supporting Data
Use ExoQuick to isolate exosomes for proteomics and miRNA profiling studies
ExoQuick helps researchers discover protein and RNA biomarkers as well as study exosome biology by enabling fast and quantitative isolation of exosomes.
ExoQuick supports exosomal protein analysis from ascites
Exosomes were isolated from ovarian tumor ascites fluid using ExoQuick, chromatography, DynaBeads, or ultracentrifugation. The ExoQuick method consistently delivered higher concentrations of protein than the other three isolation methods used (Figure 1).

Figure 1. (Top panel) Exosomal proteins were extracted from recovered exosomes, and the amount of protein determined by the Bradford microassay method (Bio-Rad Laboratories), using BSA as a standard. Proteins from each exosome isolate were standardized to the original sample volume and equal volumes were applied per lane of a 12.5% SDS-PAGE gel. (Bottom panel) Western Blotting was performed to analyze the presence of the specific marker protein, placental alkaline phosphatase (PLAP). The bound immune complexes were visualized by enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL, Amersham Life Sciences) and quantitated by densitometry (Un-Scan-it Software, Silk Scientific Corp.).
ExoQuick supports high exosomal miRNA yields
With ExoQuick, you can quickly and easily isolate high quality exosomes for miRNA analysis (Figure 2).
Exosomal microRNAs were recovered from ovarian tumor ascites fluid using either ExoQuick isolation of exosomes followed by Trizol extraction of RNA, Trizol extraction of ovarian tumor ascites fluid with no exosome isolation, or exosome purification using DynaBeads followed by Trizol extraction of RNA. The samples where exosomes were purified using ExoQuick showed the highest yields of microRNAs (Figure 2).
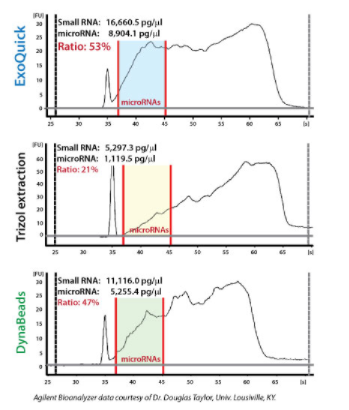
Figure 2. Recovered RNA quality and yield was assessed using a GeneQuant II. Small RNAs were analyzed with the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer Lab-on-a-Chip instrument system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA), using the Agilent Small RNA chip and reagent kit. Approximately 100 ng of isolated total RNA in 1 µl was applied to each run. The manufacturer’s recommended protocol was strictly followed to obtain Bioanalyzer profiles for the size range 6 to 150 nucleotides (nt). The profiles were calibrated for size (nt) using the small RNA ladder supplied with the kit, containing markers of 20, 40, 60, 80, and 150 nt in size, as reference. The instrument software quantitated the peak area between 0 and 150 nt as small RNA region, the area within 10 to 40 nt as miRNA region, and provides percentages of miRNA detected for each sample.
Characterizing ExoQuick exosomes with NanoSight
Exosomes purified with ExoQuick from serum show the expected particle size distribution and high concentration yields when analyzed using NanoSight’s Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA, Figure 3).

Figure 3.Exosome size distribution and yields from serum. Exosomes were purified from 50 pooled samples of normal human serum. 250 µl of serum was combined with 63 µl of ExoQuick, incubated at 4°C for thirty minutes, and pelleted by a 1500g spin for thirty minutes. The exosome pellet was resuspended in 100 µl of PBS, diluted 1:10,000, and visualized on the NanoSight LM10 instrument. The analysis shows that the ExoQuick isolation method recovered 90 nm exosomes at a concentration of of 2.74 x 1012 particles/ml.
1 Review
-
review
he ExoQuick Exosome Precipitation Solution (20 ml) is an excellent choice for researchers looking to isolate exosomes effectively from biological samples such as serum and plasma. This larger volume provides greater yield potential, allowing for the processing of multiple samples or larger volumes of fluid at once. Users appreciate the solution’s straightforward protocol, which facilitates quick and efficient exosome precipitation without the need for complex equipmenT
















