Gfp Antibody
A GFP antibody is an antibody that specifically binds to green fluorescent protein (GFP). GFP is a protein that glows green when exposed to ultraviolet light. GFP antibodies are used to detect GFP in cells and tissues. This can be useful for studying the expression and localization of GFP-tagged proteins, as well as for tracking the movement of cells and tissues.
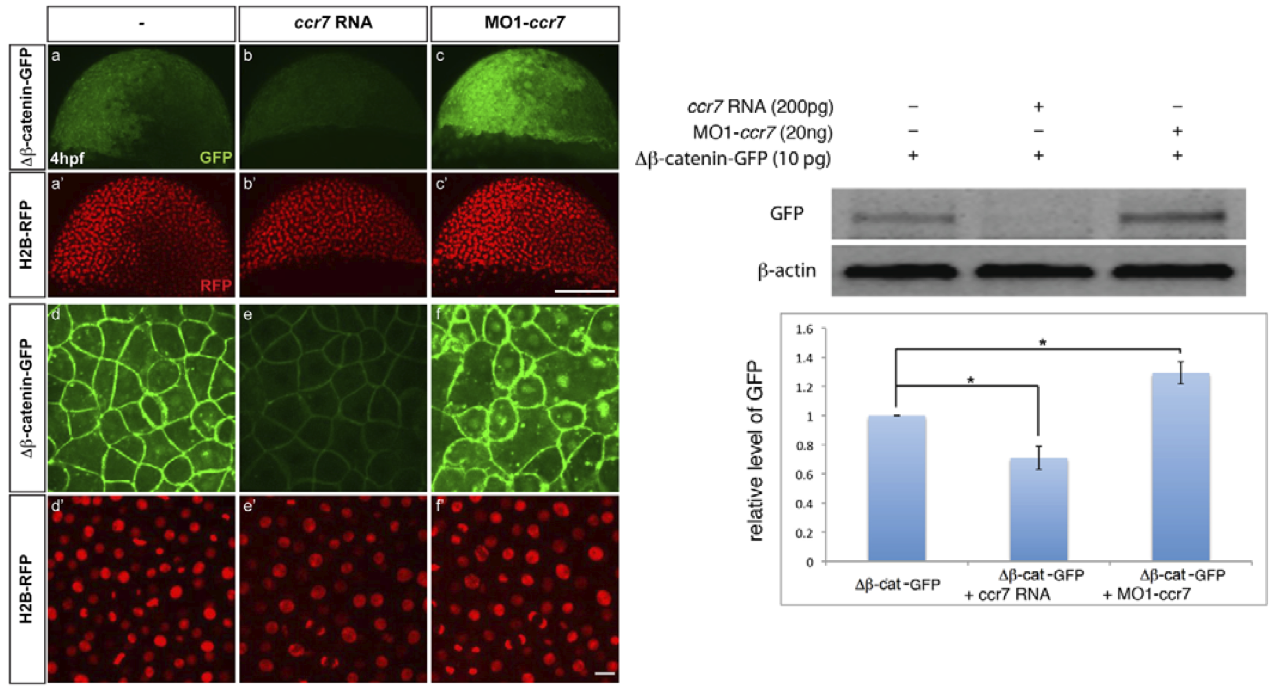
GFP antibodies are available in a variety of formats, including:
- Polyclonal antibodies: Polyclonal antibodies are produced by immunizing an animal with GFP. They recognize multiple epitopes on GFP, which makes them highly sensitive and specific.
- Monoclonal antibodies: Monoclonal antibodies are produced by fusing a hybridoma cell with a myeloma cell. They recognize a single epitope on GFP, which makes them very specific.
- Recombinant antibodies: Recombinant antibodies are produced by expressing the GFP antibody gene in a cell culture system. They are similar to monoclonal antibodies in terms of their specificity, but they are easier to produce in large quantities.
GFP antibodies can be used in a variety of applications, including:
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC): IHC is a technique used to detect proteins in tissue sections. GFP antibodies can be used to detect GFP-tagged proteins in tissue sections.
- Immunofluorescence (IF): IF is a technique used to detect proteins in cells and tissues. GFP antibodies can be used to detect GFP-tagged proteins in cells and tissues.
- Western blotting: Western blotting is a technique used to detect proteins in protein extracts. GFP antibodies can be used to detect GFP-tagged proteins in Western blots.
- Flow cytometry: Flow cytometry is a technique used to analyze cells and tissues. GFP antibodies can be used to detect GFP-tagged cells and tissues in flow cytometry.
GFP antibodies are a valuable tool for studying the expression, localization, and movement of GFP-tagged proteins. They are used in a variety of research applications, including cell biology, developmental biology, and immunology.
Here are some examples of how GFP antibodies are being used in research today:
- GFP antibodies are being used to study the development of cancer cells. Researchers are using GFP antibodies to track the movement and proliferation of cancer cells, and to identify new targets for cancer therapy.
- GFP antibodies are being used to study the immune response to infection. Researchers are using GFP antibodies to track the movement and activation of immune cells, and to identify new ways to boost the immune response to infection.
- GFP antibodies are being used to study the development of new drugs. Researchers are using GFP antibodies to screen for new drugs that can target specific cellular processes.
GFP antibodies are a powerful tool for biomedical research. They are helping us to better understand the cellular basis of disease and to develop new treatments for diseases.
