System Biosciences
Basic HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-LoxP-MCS2-MCS3-pA-LoxP-MCS4] for Gene Knock-In/Out
- SKU:
- HR100PA-1
- Availability:
- Usually Shipped in 5 Working Days
- Size:
- 10 ug
- Shipping Temperature:
- Blue Ice/ Dry Ice
Description
Basic HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-LoxP-MCS2-MCS3-pA-LoxP-MCS4] for Gene Knock-In/Out . Cat# HR100PA. Supplier: SBI System Biosciences
Knock-in any expression cassette to a specific genomic location with this basic HR targeting vector
Products

Overview

How It Works
At-a-glance—how to use an HR Targeting Vector to knock-in a gene

Figure 1. Knocking-in a gene using an HR Targeting Vector.
Step 1: Cas9 creates a double-stranded break(DSB) in the genomic DNA at a site that is complimentary to the gRNA.
Step 2: The DNA repair machinery is recruited to the DSB. In the presence of an HR Donor with homology to the region adjacent to the DSB (blue areas of the genomic and vector DNA) homologous recombination (HR) is favored over non-homologous end joining (NHEJ).
Result: The HR event leads to insertion of the region of the HR Donor Vector between the two homology arms—your gene-of-interest is integrated into the genome.
At-a-glance—how to use an HR Targeting Vector to knock-out a gene

Figure 2. Knocking-out a gene using an HR Targeting Vector.
Step 1: Cas9 creates a double-stranded break(DSB) in the genomic DNA at a site that is complimentary to the gRNA.
Step 2: The DNA repair machinery is recruited to the DSB. In the presence of an HR Donor with homology to the region adjacent to the DSB (blue areas of the genomic and vector DNA) homologous recombination (HR) is favored over non-homologous end joining (NHEJ).
Result: The HR event leads to insertion of the region of the HR Donor Vector between the two homology arms—your selection cassette is integrated into the gene, disrupting the open reading frame.

![Basic HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-LoxP-MCS2-MCS3-pA-LoxP-MCS4] for Gene Knock-In/Out Basic HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-LoxP-MCS2-MCS3-pA-LoxP-MCS4] for Gene Knock-In/Out](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-i3n9sxgjum/images/stencil/608x608/products/12477/12741/sbi%2520system%2520biosciences_1633075021__00205.original__94784.1633076533.jpg?c=1)
![Basic HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-LoxP-MCS2-MCS3-pA-LoxP-MCS4] for Gene Knock-In/Out Basic HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-LoxP-MCS2-MCS3-pA-LoxP-MCS4] for Gene Knock-In/Out](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-i3n9sxgjum/images/stencil/608x608/products/12477/12741/sbi%20system%20biosciences_1633075021__00205.original__94784.1633076533.jpg?c=1)
![Basic HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-LoxP-MCS2-MCS3-pA-LoxP-MCS4] for Gene Knock-In/Out Basic HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-LoxP-MCS2-MCS3-pA-LoxP-MCS4] for Gene Knock-In/Out](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-i3n9sxgjum/images/stencil/608x608/products/12477/15488/HR100PA-1__03435.1638779819.jpg?c=1)
![Basic HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-LoxP-MCS2-MCS3-pA-LoxP-MCS4] for Gene Knock-In/Out Basic HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-LoxP-MCS2-MCS3-pA-LoxP-MCS4] for Gene Knock-In/Out](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-i3n9sxgjum/images/stencil/100x100/products/12477/12741/sbi%20system%20biosciences_1633075021__00205.original__94784.1633076533.jpg?c=1)
![Basic HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-LoxP-MCS2-MCS3-pA-LoxP-MCS4] for Gene Knock-In/Out Basic HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-LoxP-MCS2-MCS3-pA-LoxP-MCS4] for Gene Knock-In/Out](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-i3n9sxgjum/images/stencil/100x100/products/12477/15488/HR100PA-1__03435.1638779819.jpg?c=1)

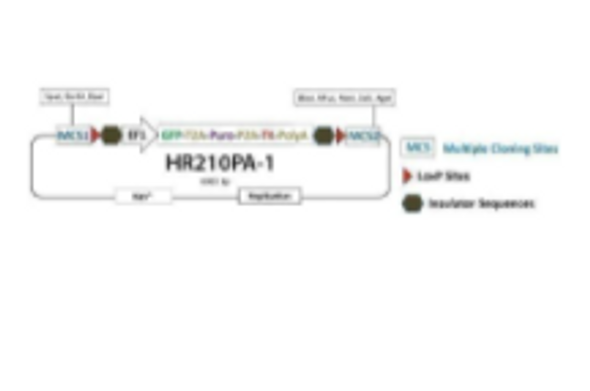


![Gene Knock-Out HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-EF1a-GFP-T2A-Puro-pA-MCS2] Gene Knock-Out HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-EF1a-GFP-T2A-Puro-pA-MCS2]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-i3n9sxgjum/images/stencil/590x590/products/12671/12936/sbi%2520system%2520biosciences_1633075021__00205.original__02911.1633076564.jpg?c=1)
![Gene Knock-Out HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-EF1a-GFP-T2A-Puro-pA-MCS2] Gene Knock-Out HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-EF1a-GFP-T2A-Puro-pA-MCS2]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-i3n9sxgjum/images/stencil/590x590/products/12671/15641/Screenshot_2021-12-09_212928__74392.1639067413.png?c=1)
![Gene Knock-Out HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-EF1α-RFP-T2A-Puro-pA-MCS2] Gene Knock-Out HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-EF1α-RFP-T2A-Puro-pA-MCS2]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-i3n9sxgjum/images/stencil/590x590/products/12673/12938/sbi%2520system%2520biosciences_1633075021__00205.original__03121.1633123705.jpg?c=1)
![Gene Knock-Out HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-EF1α-RFP-T2A-Puro-pA-MCS2] Gene Knock-Out HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-EF1α-RFP-T2A-Puro-pA-MCS2]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-i3n9sxgjum/images/stencil/590x590/products/12673/15643/Screenshot_2021-12-09_214631__77660.1640262373.png?c=1)
![Gene Knock-Out HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-EF1a-RFP-T2A-Hygro-pA-MCS2] Gene Knock-Out HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-EF1a-RFP-T2A-Hygro-pA-MCS2]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-i3n9sxgjum/images/stencil/590x590/products/12672/12937/sbi%2520system%2520biosciences_1633075021__00205.original__32636.1633076564.jpg?c=1)
![Gene Knock-Out HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-EF1a-RFP-T2A-Hygro-pA-MCS2] Gene Knock-Out HR Targeting Vector [MCS1-EF1a-RFP-T2A-Hygro-pA-MCS2]](https://cdn11.bigcommerce.com/s-i3n9sxgjum/images/stencil/590x590/products/12672/15642/Screenshot_2021-12-09_213653__16327.1639067857.png?c=1)