System Biosciences
PinPoint-HR attP Placement Vector – Empty MCS for cloning HR Arms
- SKU:
- PIN400A-1
- Availability:
- Usually Shipped in 5 Working Days
- Size:
- 10ug
- Shipping Temperature:
- RT/Blue Ice/ Dry Ice
Description
PinPoint-HR attP Placement Vector – Empty MCS for cloning HR Arms. Cat# PIN400A. Supplier: SBI System Biosciences</
- Create isogenic cell lines
- Achieve high-efficiency integration with no insert size-limit
- Turn cell line construction into a high-throughput process
Products

Overview

- Create isogenic cell lines
- Achieve high-efficiency integration with no insert size-limit
- Turn cell line construction into a high-throughput process
How It Works
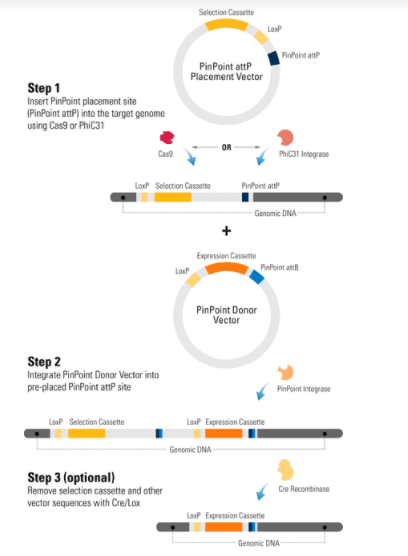
Placing a PinPoint attP site using the CRISPR/Cas9 System
To use the PinPoint-HR attP Placement Vector with MCS to place a PinPoint attP site at a specific location, you must first clone homology regions into the 3’ and 5’ MCSs of the PinPoint-HR attP Placement Vector. The homology regions should be adjacent to the site targeted by the Cas9 gRNA. Then co-transfect the PinPoint-HR attP Placement Vector with any of SBI’s Cas9 SmartNuclease and gRNA systems. Insertion follows the basic gene knock-in process (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Knocking-in a gene using an HR Targeting Vector. Step 1: Cas9 creates a double-stranded break(DSB) in the genomic DNA at a site that is complimentary to the gRNA. Step 2: The DNA repair machinery is recruited to the DSB. In the presence of an HR Donor with homology to the region adjacent to the DSB (blue areas of the genomic and vector DNA) homologous recombination (HR) is favored over non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). Result: The HR event leads to insertion of the region of the HR Donor Vector between the two homology arms—your gene-of-interest is integrated into the genome.
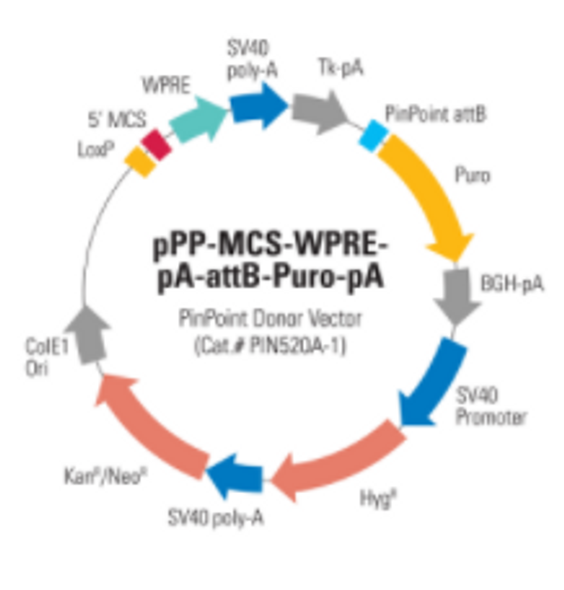
After using the CRISPR/Cas9 System to place the PinPoint attP site at your desired location, you can use the PinPoint Integrase and a PinPoint Donor Vector to insert your gene-of-interest into the PinPoint attP site. A third optional step involves removal of extra vector sequences using the Cre/Lox system, leaving behind only your expression cassette and a single LoxP site.
Additional advantages to using the CRISPR/Cas9 System for placing the PinPoint attP site
If you choose to use the PinPoint-HR attP Placement Vector to insert the PinPoint attP site, the PGK promoter on the Placement Vector combines with the promoterless puromycin marker on any of SBI’s PinPoint Donor Vectors, to enable puromycin selection only if the PinPoint Donor Vector integrates at the correct site.
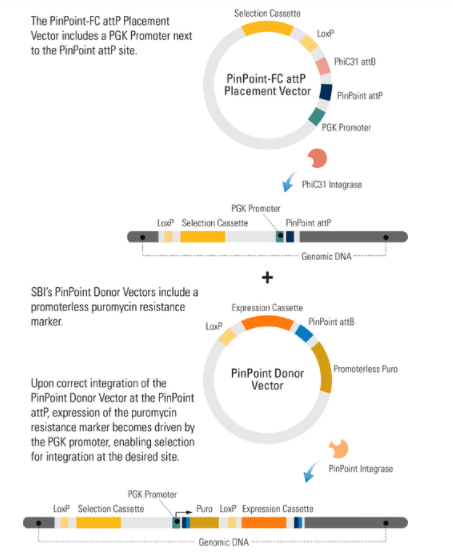
Supporting Data
See the PinPoint Targeted Integration System in action
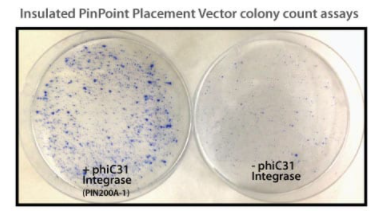
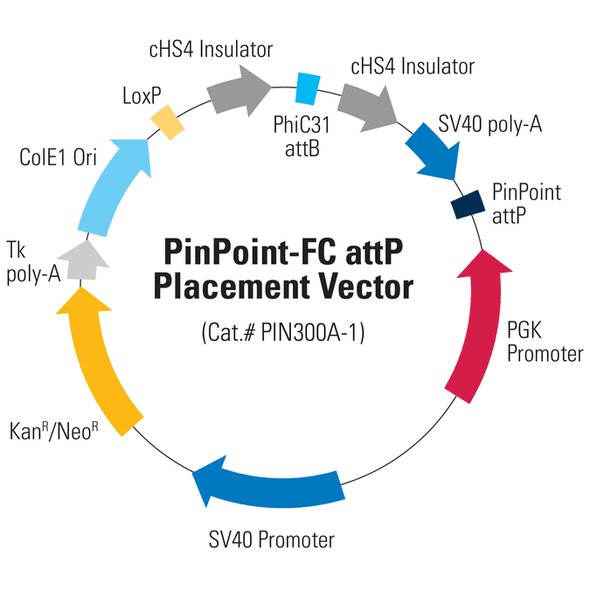
Figure 1. Efficient placement of the PinPoint attP site using the PhiC31 System. Step 1 of the PinPoint Targeted Integration System—the PinPoint attP site was placed into HEK293 cells using the PinPoint-FC Placement Vector (Cat.# PIN300A-1) and the PhiC31 Integrase (Cat.# FC200PA-1). Positive cells were selected with G418 (neomycin resistance) for fourteen days and six separate lines were picked and expanded. After eleven days, the cells were fixed and stained with a solution of 50% methanol plus 1% methylene blue. The plates were washed twice with PBS and allowed to air dry. Only the plate of cells that were transfected with the PhiC31 Integrase Expression Plasmid showed a robust number of cells.
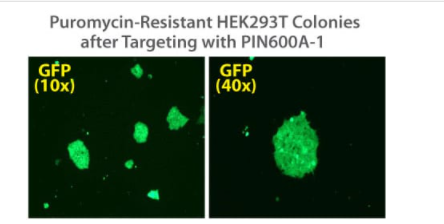
Figure 2. Targeted integration with the PinPoint Integrase and a PinPoint Donor Plasmid. Step 2 of the PinPoint Targeted Integration System—the cell lines created in Figure 1 were transfected with a Positive Control PinPoint Gene Donor Vector expressing GFP (Cat.# PIN600A-1) for precise integration. Unlike the R4 integrase used in a similar system, the PinPoint Integrase does not recognize pseudo-sites and will only integrate at its placed recognition sequence. This feature results in the increased efficiency of correctly retargeted cell lines compared to the R4 integrase system. The entire therapeutic gene expression cassette is active and fully insulated with cHS4 DNA elements.

Figure 3. The PinPoint Integrase mediated specific placement of the PinPoint Donor Vector. We used a junction PCR assay to verify that the PinPoint Donor Vector was integrated at the correct site targeted to the correct site, amplifying across the PinPoint attL site (after PinPoint mediated integration, the plasmid-borne PinPoint attP and attB sites become genomic attL and attR sites). The appearance of bands in the L1, L2, and L3 lanes only indicate the predicted, PinPoint Integrase-mediated insertion of the PIN600A-1 Donor Vector at the placed PinPoint attP site with high precision.