System Biosciences
ExoQuick TC 50 ml
- SKU:
- EXOTC50A-1
- Availability:
- Usually Shipped in 5 Working Days
- Size:
- 50 ml
- Shipping Temperature:
- RT or Blue Ice
Description
ExoQuick TC 50ml. Cat# EXOTC50A. Supplier: SBI System Biosciences


Overview
A better way to isolate exosomes
"We therefore pursued the ExoQuick® method for further study, as these samples required much less sample input, a key benefit when working with clinical samples and mouse models1."
Need exosomes? SBI's ExoQuick-TC enables high-throughput, quantitative isolation of exosomes from low volumes (as little as 1 ml) of tissue culture media and certain biofluids (saliva, urine, follicular fluid, and breast milk). Note, to isolate exosomes from serum, plasma, or ascites fluid, use the original ExoQuick formulation (EXOQ5A-1 or EXOQ20A-1)). Compatible with a wide variety of downstream applications, ExoQuick-TC is an effective and proven alternative to ultracentrifugation1-3.
ExoQuick-TC’s fast, ultracentrifugation-free method:
- Saves time and labor
- Is easily scalable
- Conserves precious sample
- Delivers high yields of functional, high quality exosomes
- Can be used to isolate exosomes for a wide range of downstream applications, including
- Biomarker studies
- Exosomal miRNA profiling
- Exosomal proteomics
- Exosomal lipidomics/metabolomics
- Functional studies, such as in cell-to-cell signaling
- Basic biology, such as role in tumorigenesis
ExoQuick-TC is a proprietary polymer that gently precipitates exosomes. First, pre-clear your samples of cells and cellular debris, and then simply add the appropriate amount of ExoQuick-TC to your cleared biofluid, refrigerate, and centrifuge (see the product manual for protocol details). Your exosomes will be in the pellet, ready for resuspension in an appropriate solution.

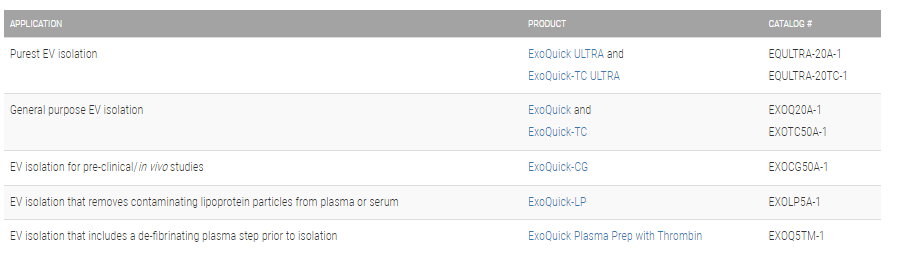
Choose the right ExoQuick for your application:
REFERENCES
Chugh PE, et al. Systemically Circulating Viral and Tumor-Derived MicroRNAs in KSHV-Associated Malignancies. PLoS Pathog. 2013.
9
(7): e1003484. PMCID: PMC3715412.
Umezu T, et al. Leukemia cell to endothelial cell communication via exosomal miRNAs. Oncogene. 2013 May 30.
32
(22):2747-55. PMID: 22797057.
Sohel MM, et al. Exosomal and Non-Exosomal Transport of Extra-Cellular microRNAs in Follicular Fluid: Implications for Bovine Oocyte Developmental Competence. PLoS One. 2013 Nov 4.
8
(11):e78505. PMCID: PMC3817212.
Antes T, et al. Methods for Microvesicle Isolation and Selective Removal. Patent No.: US 9,005,888 B2.
How It Works
High-throughput, quantitative exosome recovery
ExoQuick-TC can be used to purify exosomes from a wide variety of tissue culture media4, and from certain biofluids such as saliva1, urine2, follicular fluid3, and breast milk5. With a simple workflow involving minimal hands-on time and low input sample volume requirements, ExoQuick-TC is an excellent option for researchers who need to purify multiple exosome samples.
To isolate exosomes from tissue culture media, simply:
- Add an appropriate volume of ExoQuick-TC
- Incubate overnight at 4°C
- Isolate exosomes with a 30-minute low-speed spin (1500g).
Isolated exosomes can be found in the pellet and resuspended in an appropriate solution.

You can verify the presence of exosomes with a number of different methods, including Western blotting for general exosome markers (CD63, CD9, CD81, and HSP70), NanoSight analysis, or EM (learn about different ways to detect exosomes and more in our Exosome Basics Guide).
The Bottom Line
With ExoQuick-TC, you can obtain high-quality exosomes from tissue culture media and certain biofluids using a protocol that can easily be performed on multiple samples and requires very low volumes of input sample.
REFERENCES
Yang J, et al. Detection of Tumor Cell-Specific mRNA and Protein in Exosome-Like Microvesicles from Blood and Saliva. PLoS ONE. 2014. 9(11): e110641. PMCID: PMC 4232306.
Alvarez ML. Isolation of urinary exosomes for RNA biomarker discovery using a simple, fast, and highly scalable method. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. 1182:145-70. PMID: 25055908.
Sohel MM, et al. Exosomal and Non-Exosomal Transport of Extra-Cellular microRNAs in Follicular Fluid: Implications for Bovine Oocyte Developmental Competence. PLoS One. 2013 Nov 4. 8(11):e78505. PMCID: PMC3817212.
Zhu L, et al. Novel method for extracting exosomes of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2014 June 7. 20(21): 6651-6657. PMCID: PMC4047354.
Gu Y, et al. Lactation-Related MicroRNA Expression Profiles of Porcine Breast Milk Exosomes. PLoS ONE. 2012. 7(8): e43691. PMCID: PMC3427246.
Supporting Data
Characterizing ExoQuick-TC exosomes with NanoSight
Exosomes purified with ExoQuick-TC from tissue culture media show the expected particle size distribution and high concentration yields when analyzed using NanoSight’s Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA, Figure 1).
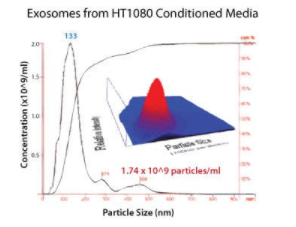
Figure 3.Exosome size distribution and yields from tissue culture media. Cells from a human HT1080 lung sarcoma cell line were cultured in conditioned media (serum-free) for 72 hours. 10 mL of media was combined with 2 mL ExoQuick-TC, incubated overnight at 4°C, and centrifuged at 1500g for 30 minutes to isolate exosomes. The exosome pellet was resuspended in 1 mL PBS, diluted 1:40, and visualized on the NanoSight LM10 instrument. The analysis shows that ExoQuick-TC recovered 133 nm exosomes at a concentration of 1.74 x 109 particles/mL.
1 Review
-
Review of the The ExoQuick TC (50 ml)
The ExoQuick TC (50 ml) is an excellent tool for exosome research! This kit provides a reliable and straightforward method for isolating exosomes from tissue culture media, yielding high-quality results every time. The protocol is easy to follow, which makes the isolation process quick and efficient. I've successfully used ExoQuick TC with various cell lines, and the purity of the isolated exosomes has consistently exceeded my expectations














